Curriculum
🎯 "Science 10X – Your 5-Step Board Exam Success Plan!"
Chapter 1 : Chemical Reactions and Equations
0/3Chapter 11 : Electricity
0/5Chapter 5 : Life Process
0/1Control and Coordination
0/1Chemical Reactions and Equations| | Most Probable Exam ready objective Questions
Objective Qs (1 mark)
1. A dilute ferrous sulphate solution was gradually added to a beaker containing an acidified permanganate solution. The light purple colour of the solution fades and finally disappears. Which of the following is the correct explanation for the given observation?
(a) $\mathrm{KMnO}_4$ is an oxidising agent, it oxidises $\mathrm{FeSO}_4$.
(b) $\mathrm{FeSO}_4$ acts as an oxidising agent and oxidises $\mathrm{KMnO}_4$.
(c) The colour disappears due to dilution; no reaction is involved.
(d) $\mathrm{KMnO}_4$ is an unstable compound and decomposes in the presence of $\mathrm{FeSO}_4$ to a colourless compound.
2. Which of the following is NOT a physical change?
(a) Boiling of water to give water vapour.
(b) Melting of ice to give water.
(c) Dissolution of salt in water.
(d) Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
3. Which information is NOT conveyed by a balanced chemical equation?
(a) Physical states of reactants and products.
(b) Symbols and formulae of all the substances involved in a particular reaction.
(c) Number of atoms/molecules of the reactants and products formed.
(d) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not.
[DIKSHA]
5. Which of the following processes involve chemical reactions?
(a) Storage of oxygen gas under pressure in a gas cylinder.
(b) Liquefaction of air.
(c) Keeping petrol in a china dish in the open.
(d) Heating a copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
6. Which of the following are double displacement reactions?
(I) $\mathrm{Pb}+\mathrm{CuCl}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbCl}_2+\mathrm{Cu}$
(II) $\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+\mathrm{BaCl}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{BaSO}_4+2 \mathrm{NaCl}$
(III) $\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{CO}_2$
(IV) $\mathrm{CH}_4+2 \mathrm{O}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{CO}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
Options:
(a) (I) and (IV)
(b) Only (II)
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (III) and (IV)
8. Solid calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form calcium hydroxide accompanied by liberation of heat. This process is called slaking of lime. Calcium hydroxide dissolves in water to form a solution called lime water. Which of the following is true for slaking lime and the solution formed?
(I) It is an endothermic reaction.
(II) It is an exothermic reaction.
(III) The pH of the resultant solution is greater than 7.
(IV) The pH of the resultant solution is less than 7.
Options:
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (IV)
(d) (III) and (IV)
9. Barium chloride on reacting with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of reaction?
(I) Displacement reaction
(II) Precipitation reaction
(III) Combination reaction
(IV)Double displacement reaction
Options:
(a) (I) only
(b) (II) only
(c) (IV) only
(d) (II) and (IV) only
Case Based Qs (4 marks)
10. A 2 cm long thin ribbon of a metal ‘ $X$ ‘ was taken and first cleaned with a sandpaper. It was then burnt using a spirit lamp or a burner by holding it with a pair of tongs. The ribbon burnt with a dazzling white flame and formed a powder ‘ $\gamma$ ‘ which was collected in a watch glass.
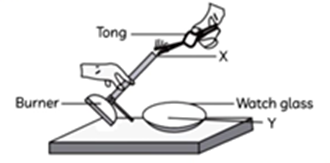
(A) Which option correctly identifies both X and $Y$ ?
|
|
X |
Y |
|
(a) |
Magnesium |
Magnesium carbonate |
|
(b) |
Aluminium |
Aluminium oxide |
|
(c) |
Magnesium |
Magnesium oxide |
|
(d) |
Iron |
Iron oxide |
(B) The colour of powder or ash formed when a magnesium ribbon is burnt in air:
(a) grey
(b) black
(c) white
(d) yellow
(C) Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
OR
(C) Is burning of magnesium ribbon a physical change or a chemical change? Justify your answer.
(D) Assertion (A): Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame.
Reason ( R ): When magnesium ribbon burns in air, only heat is evolved.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
11. Amit took two boiling tubes. He added about 2 grams of a green coloured metal salt ‘A’ in the first tube and 2 grams of a white coloured metal salt ‘ $B$ ‘ in the second tube. Both the tubes were heated by holding them with a pair of tongs. The smell of burning sulphur was observed in first test tube, whereas brown gas was emitted in the second test tube.
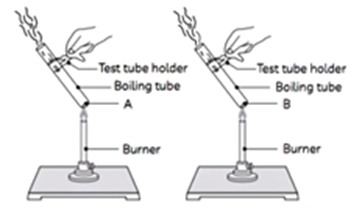
(A) The salts ‘ $A$ ‘ and ‘ $B$ ‘ are:
(a) ferrous nitrate and lead sulphate, respectively.
(b) ferric oxide and lead nitrate, respectively.
(c) ferrous sulphate and lead nitrate, respectively.
(d) ferric oxide and lead sulphate, respectively.
OR
(A) Assertion (A): Green coloured ferrous sulphate crystals on heating first changes to dirty white and then to brownish black.
Reason (R): Ferrous sulphate crystals contain seven molecules of water of crystallisation.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(B) What are the products formed when green coloured metal salt ‘ $A$ ‘ is heated?
(C) On heating white coloured metal salt ‘B’, two gases are evolved, one is colourless and the other is brown in colour. Which gases are these?
(D) In which of the following category will you put the reaction of heating ferrous sulphate and lead nitrate?
(I) Decomposition reaction
(II) Combination reaction
(III) Endothermic reaction
(IV) Exothermic reaction
Options:
(a) Only (l)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (III) (d) Both (II) and (IV)
Short Answer ( 2 & 3 )
13. Ferrous sulphate decomposes with the evolution of a gas having a characteristic odour of burning sulphur. Write the chemical reaction involved and identify the type of reaction.
14. Why do fireflies glow at night?
16. A substance $X$, which is an oxide of a group 2 element, is used intensively in the cement industry. This element is present in bones also. On treatment with water, it forms a solution which turns red litmus blue. Identify X and also write the chemical reactions involved.
17. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
18. A magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen to give a white compound X accompanied by emission of light. If the burning ribbon is now placed in an atmosphere of nitrogen, it continues to burn and forms a compound Y .
(A) Write the chemical formulae of $X$ and $Y$.
(B) Write a balanced chemical equation, when X is dissolved in water.
19. Zinc liberates hydrogen gas when reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, whereas copper does not. Explain why.
20. During the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid, the following observations were made:
(A) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium (Al) is added.
(B) Some bubbles of a gas are seen when lead $(\mathrm{Pb})$ reacts with the acid.
Explain these observations giving suitable reasons.
21. A silver article generally turns black when kept in the open for a few days. The article when rubbed with toothpaste again starts shining.
(A) Why do silver articles turn black when kept in the open for a few days? Name the phenomenon involved.
(B) Name the black substance formed and give its chemical formula.
22. Complete the missing components/variables given as $X$ and $Y$ in the following:
(A) $\mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_{2(o q)}+2 \mathrm{KI}_{(o q)} \rightarrow \mathrm{PbI}_2(\mathrm{X})+2 \mathrm{KNO}_3(\mathrm{Y})$
(B) $\mathrm{Cu}_{(a)}+2 \mathrm{AgNO}_{3(a q)} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_{2(a q)}+\mathrm{X}_{(a)}$
(C) $\mathrm{Zn}_{(\mathrm{s})}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_{4(\mathrm{aq})} \rightarrow \mathrm{ZnSO}_4(\mathrm{X})+\mathrm{H}_2(\mathrm{Y})$
(D) $\mathrm{CaCO}_{3(s)} \xrightarrow{x} \mathrm{CaO}_{(s)}+\mathrm{CO}_{2(g)}$
Long Answer Type Qs (5 marks)
23. You are provided with two containers made up of copper and aluminium. You are also provided with solutions of dilute HCl , dilute $\mathrm{HNO}_3, \mathrm{ZnCl}_2$ and $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$. In which of the containers can these solutions be kept?
24. (A) Why cannot a chemical change be normally reversed?
(B) Why is it always essential to balance a chemical equation?
(C) What happens when $\mathrm{CO}_2$ gas is passed through lime water and why does it disappear on passing excess $\mathrm{CO}_2$ ?
(D) Can rusting of iron take place in distilled water?
[DIKSHA]
26. On heating blue-coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate in a boiling tube, copper oxide (black), oxygen gas and a brown gas X is formed.
(A) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
(B) Identify the brown gas $X$ evolved.
(C) Identify the type of reaction.
(D) What could be the pH range of aqueous solution of the gas $X$ ?